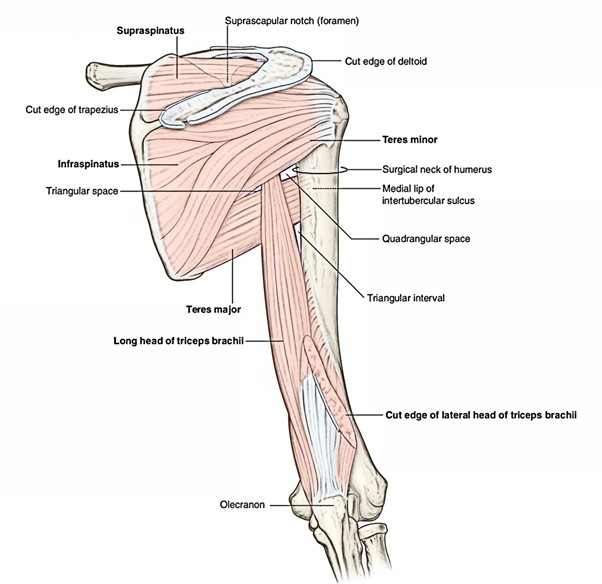
The Supraspinatus is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that make up the rotator cuff. The supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles starts from 2 large fossae, 1 above and 1 below the spine, on the posterior surface of the scapula. They create tendons that insert on the greater tubercle of the humerus.
Supraspinatus
Origin
Supraspinatus originates from medial 2/3rd of the supraspinous fossa of the scapula.
Insertion
The fibres pass forward and converge under the acromion, into a tendon, which crosses above the shoulder joint and is inserted on to the superior facet on the greater tubercle of the humerus.
Nerve Supply
Supraspinatus is supplied by the suprascapular nerve (C5 and C6).
Actions
- Supraspinatus initiates the abduction of shoulder. It’s responsible for first 15° of abduction of the shoulder and thus assists the deltoid in carrying abduction thereafter, i.e, from 15° to 90°.
Clinical Testing
- The supraspinatus can be palpated deep to the trapezius and above the spine of the scapula when the arm is abducted against the resistance.
Clinical significance
Rupture of supraspinatus tendon: It’s a common soft tissue injury in the shoulder region. The patient with ruptured supraspinatus tendon when asked to raise his hand above the head on the affected side, he’ll first tilt his body on the affected side in order that arm swings far from the body leading to an initial abduction of 15° or he’ll somewhat (about 15°) raise the affected arm by the hand of the healthy side—a common ‘trick- device’ learned by the patients with ruptured supraspinatus tendon.
Infraspinatus
It’s a thick triangular muscle, which takes up majority of the infraspinous fossa.
Origin
It originates from the medial 2/3rd of the fossa by tendinous fibres from ridges on its surface.
Insertion
Its fibres converge to create a tendon, which enters across the posterior aspect of the shoulder joint to be inserted on to the middle facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus.
Nerve Supply
Infraspinatus is supplied by the suprascapular nerve (C5 and C6).
Action
Infraspinatus is the lateral rotator of the humerus.
Clinical Testing
The infraspinatus can be palpated inferior to the spine of the scapula when the arm is laterally rotated against the resistance.

 (60 votes, average: 4.75 out of 5)
(60 votes, average: 4.75 out of 5)