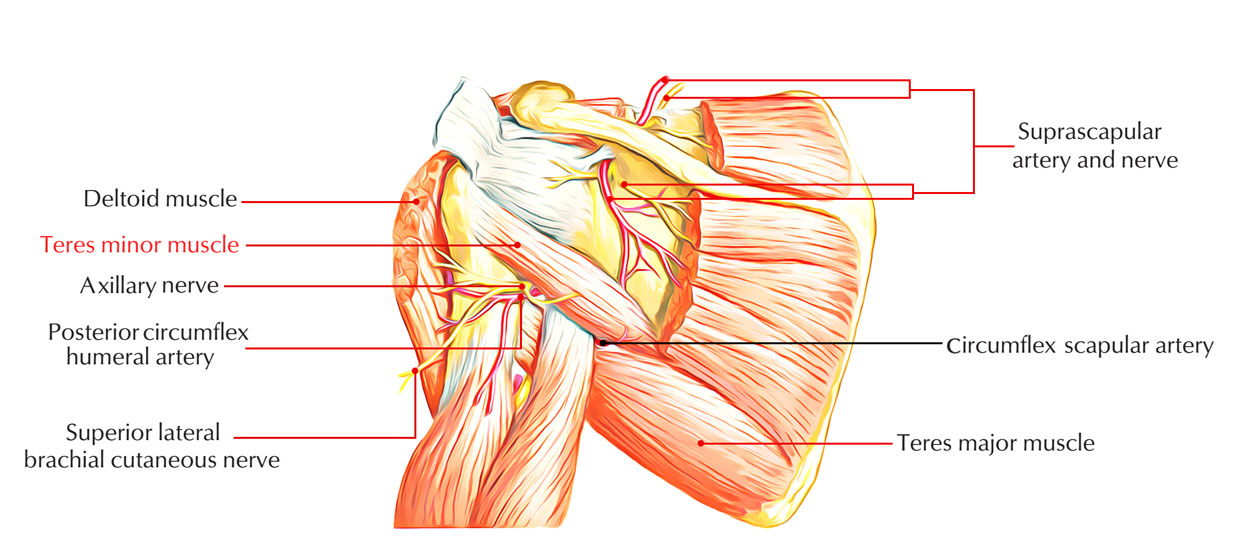
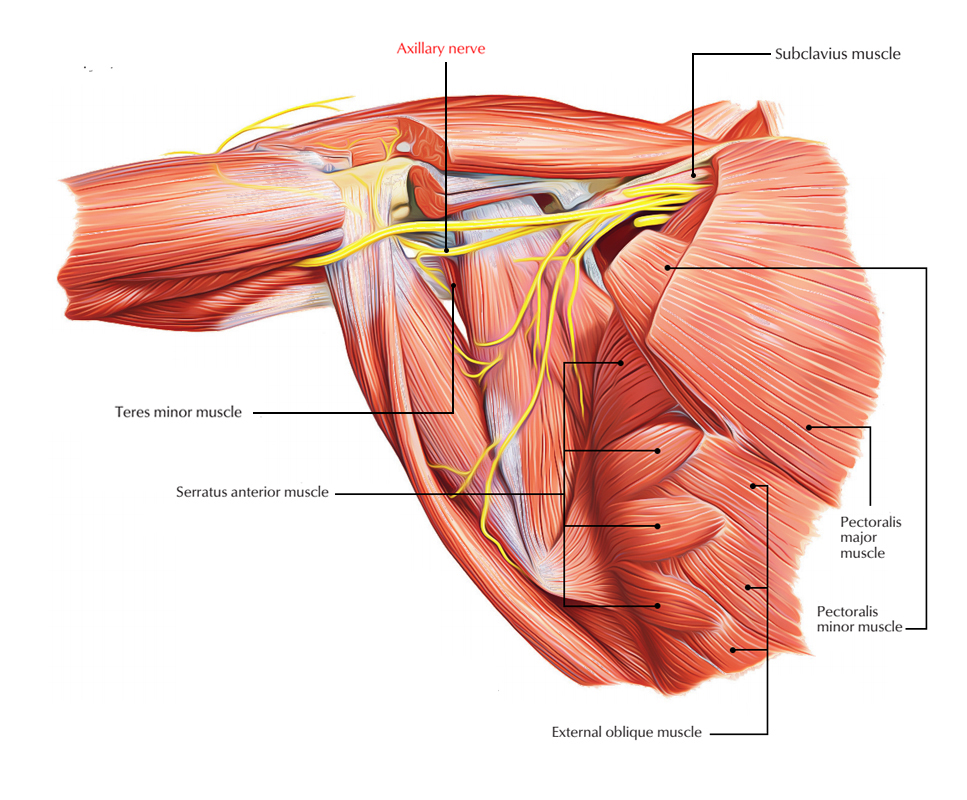
Teres minor is among the four muscles that contribute to the making of the Rotator Cuff. Its shape is long and narrow and sometimes it may blend into infraspinatus. The primary function of teres minor is to keep the humerus steady in the glenoid fossa in the shoulder movement.
Origin
The Teres minor muscles originates from the upper two-thirds of the lateral border of the scapula. Some physicians also consider its origin from the two aponeurotic laminae since the first one aponeurotic laminae separate the muscle from the infraspinatus muscle and the other from the teres major muscle.
Insertion
- The upper fibres of the teres minor muscle end up in a tendon which inserts into the inferior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus.
- The lower fibres of the teres minor muscle insert into the humerus directly below the inferior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus.
Nerve Supply of Teres Minor Muscle
Teres Minor is innervated by a branch of axillary nerve (roots C5, C6) from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus.
Blood Supply of Teres Minor Muscle
The circumflex scapular artery and the posterior circumflex humeral artery are the carrier of the blood for the teres minor muscle.
Actions of Teres Minor Muscle
Teres minor along with Infraspinatus is responsible for external rotation of the shoulder joint. It helps in adduction and extension of the shoulder as well.
It stabilizes the head of the humerus against the upward pull of the deltoid during the abduction.