Its body, which is prismatic and also triangular, as well as a little rounded inwards at its anterior part, provides a convex superior surface, split into two sections by a prominent line, which offers connection to the second as well as third dorsal interosseous muscles; two lateral surfaces, which represent the very same muscles; and an inferior edge, which is thin, scooped, and grants attachment to the first plantar interosseous muscle. It is a little shorter than the second, however provides almost the exact same kind.
Structure
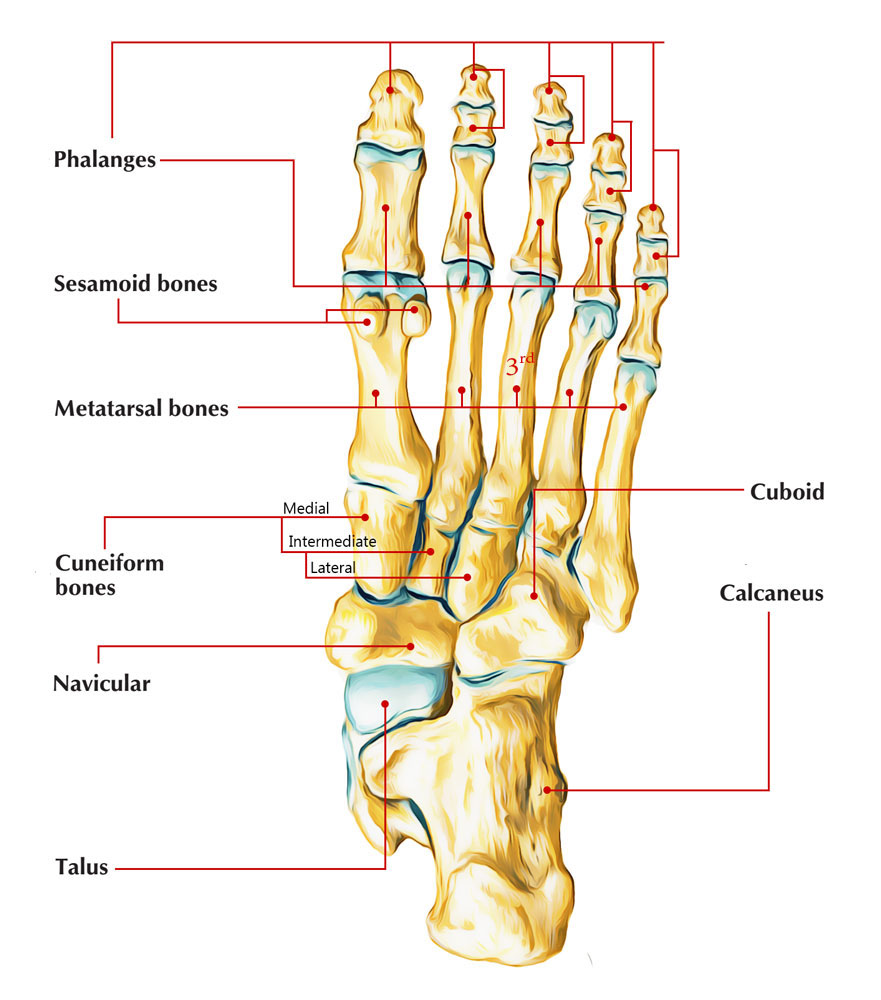
The Third Metatarsal
- Its posterior or tarsal extremity is almost of the exact same type as that of the preceding bone.
- It provides posteriorly a flat triangular surface, directed inwards, which integrates with the third cuneiform bone; internally, two small surfaces, constant posteriorly, however apart anteriorly by a small depression, and which integrate with the second metatarsal bone; externally, a small concave surface which is gotten in touch with the fourth metatarsal bone, and which is restricted below by impressions of ligaments.
- The base of this extremity is turned upwards, structurally flat and rough; its top, which is downwards, offers attachment to ligaments.
- The anterior or phalangeal extremity of this particular bone looks like one of the preceding, and is integrated to the first phalanx of the third toe.
Clinical Significance
Injuries
- The four lesser metatarsals supply only one contact point each on the plantar weight-bearing surface.
- Considerable ligamentous structures connect each of the bones to their nearby next-door neighbors.
- Fractures of the central metatarsals are far more common than separated first metatarsal fractures. Central metatarsal fractures might be separated injuries or part of a more substantial injury pattern.
- Indirect twisting systems might lead to a spiral pattern. One should watch out for injury with participation of base of second metatarsal.
- Many separated specific central metatarsal fractures can be dealt with closed with hard-soled shoes and escalating weight bearing as endured.
- The surgical requirement usually discussed is any fracture showing more than 10 degrees of discrepancy in the dorsal plantar plane or 3 to 4 mm translation in any plane.
- Issues of dealing with central metatarsal fractures normally originate from insufficient remediation of plantar anatomy.

 (49 votes, average: 4.66 out of 5)
(49 votes, average: 4.66 out of 5)