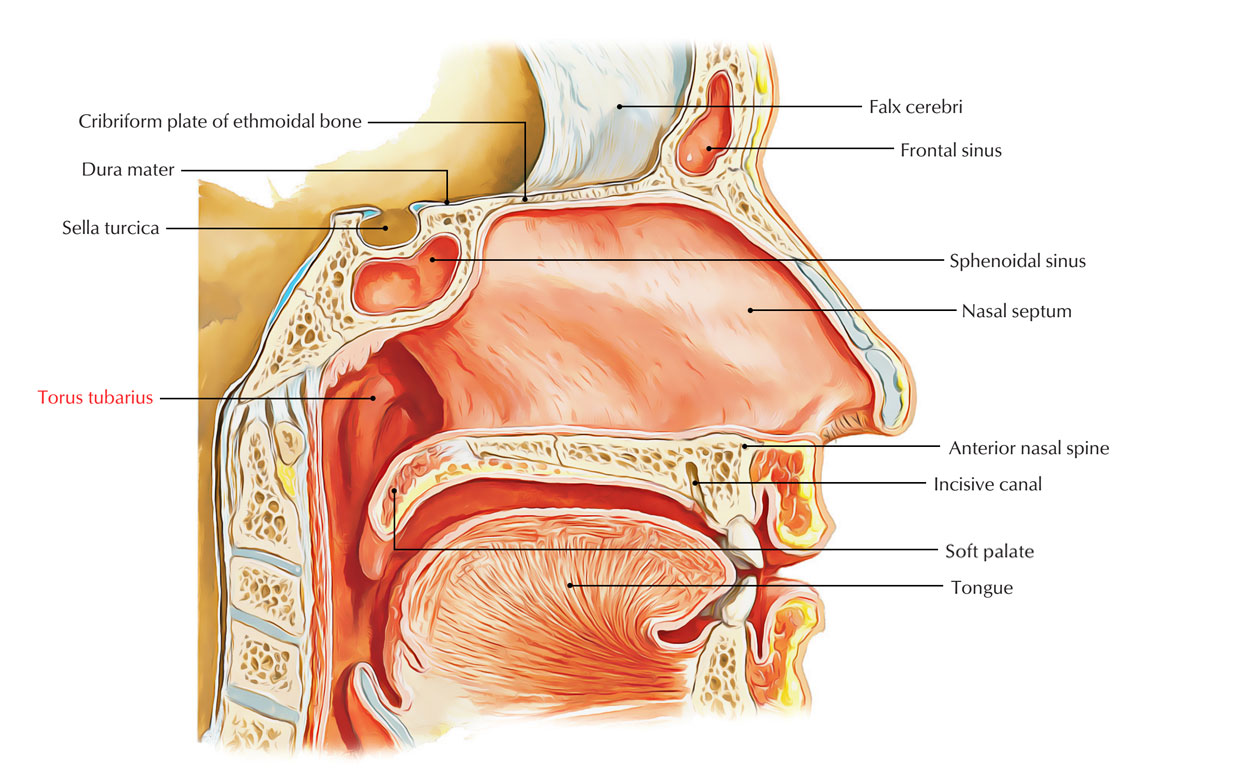
Torus tubarius or cushion of the auditory canal is a mucosal elevation in the lateral aspect of the nasopharynx, which is formed by the underlying pharyngeal end of the cartilaginous portion of the Eustachian tube behind the pharyngeal orifice of the tube. The opening of the Eustachian tube is anterior to the torus tobarius.
Torus Tubarius
The fossa of Rosenmuller is just posterior to the torus tubarius. The torus tubarius is quite close to the tubal tonsil which is often referred as the tonsil of (the) torus tubarius. Assosiating the torus with its tonsil might be seen as incorrect.
Folds
From the inferior portion of the torus tubarius, two mucosal folds are extended which are named anterior fold and posterior fold.
Posterior Fold
The posterior fold is the vertical fold of mucous membrane which is also called the salpingopharyngeal fold. It stretches from the lower part of the torus tubarius and includes the Salpingopharyngeus muscle which emerges from the superior border of the medial lamina of the cartilage of the auditory tube and passes downward and then blends with the posterior fasciculus of the palatopharyngeus muscle.
Anterior Fold
The Anterior Fold is the second and smaller fold which is also called the salpingopalatine fold and is smaller than the salpingopharyngeal fold. It includes some fibers of muscle, called salpingopalatine muscle and stretches from the superior border of lateral lamina of the cartilage, anteroinferiorly, to the back of the hard palate.
The tensor veli palatini does not contribute to the fold, because the origin of tensor veli palatine is deep to the cartilaginous opening.

 (47 votes, average: 4.81 out of 5)
(47 votes, average: 4.81 out of 5)