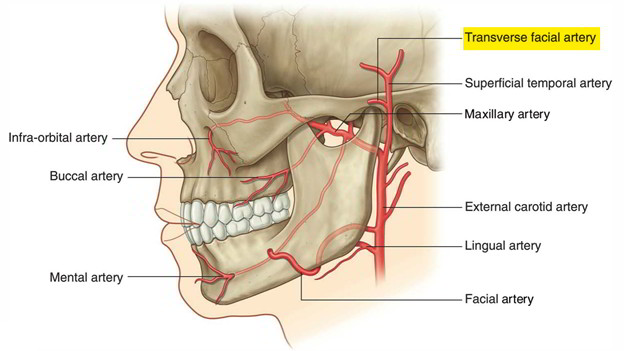
It supplies anterolateral aspect of the face. Commencement from the superficial temporal artery within the parotid gland.
The transverse facial artery is in a transitional position relative to the vessels of the scalp and those of the face proper. It is involved in the equilibrium between these two systems. It usually arises directly from the external carotid artery, and therefore would deserve the status of terminal branch with the superficial temporal and maxillary arteries. It courses superficial to the masseteric muscle below the zygomatic arcade and follows the parotid duct to its orifice opposite the superior third molar on the same side. In addition to the masseteric branch already described, the transverse facial artery also gives branches to the anterior zygomatic area and branches anastomosed with the zygomatico-orbital artery or the vessel which replaces it. At the inferior rim of the orbit, it anastomoses with the corresponding branches coming from the facial and maxillary arteries. In case of hypoplastic facial or distal maxillary arteries, it represents one possible hemodynamic solution to supplying the nasolabial region. Its distinguishing characteristics are its course parallel to the internal maxillary artery, its crossing at right angles with the buccal artery, and its anastomoses with this vessel anteriorly.
Course
It emerges out of the anterior border of the parotid gland. It passes forwards in the face. It is situated above the parotid duct.
It runs along with the upper buccal branch of facial nerve. Termination
It terminates by anastamosing with facial and infra orbital arteries.
Branches
- Glandular branches to the parotid gland.
- Muscular branches to masseter
- Cutaneous branches to the anterolateral aspect of middle of the face.

 (48 votes, average: 4.63 out of 5)
(48 votes, average: 4.63 out of 5)