The transversus thoracis muscles are on the same level as the innermost intercostals and are located in the deep surface of the anterior thoracic wall.
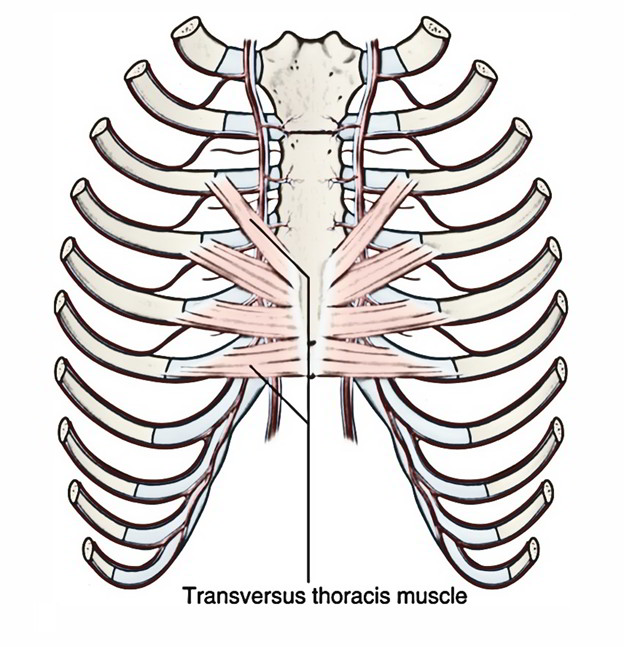
Transversus Thoracis Muscles
Origin
The transversus thoracis muscles emerge from:
- The posterior side of the xiphoid process.
- The inferior portion of the sternum.
- The adjacent costal cartilages of the lower true ribs.
Insertion
The transversus thoracis muscles are located deep towards the internal thoracic vessels and also attach these vessels towards the wall. In order to insert within the inferior margins of the costal cartilages of ribs III to VI they travel superiorly as well as laterally. Probably, they draw these latter parts inferiorly.
Blood supply
Transversus thoracis muscles are supplied by anterior and posterior intercostal arteries.
Nerve supply
Transversus thoracis muscles are innervated by intercostal nerves.
Action
The transverse thoracis muscle supports expiration by drawing the ribs cranially.
Divisions
The transversus thoracis muscle is divided into the following three parts:
- Intercostalis intimus.
- Subcostalis.
- Sternocostalis.
Intercostalis intimus
It emerges via the inner surface of the rib above and attaches on the inner surface of the rib below. It occupies the middle two-fourth of the intercostal space. It is innervated by intercostal nerve of the same space. At the time of expiration intercostalis intimus elevates the ribs.
Subcostalis
Subcostalis emerges via the inner side of rib near the angle and attaches on the inner surface of the 2nd or 3rd rib below. It is located within the posterior part of the intercostal space on the same level as the intercostalis intimus. It interferes among the intercostal nerve and vessels, along with pleura. It is innervated by intercostal nerves. It helps in depression of the ribs.
Sternocostalis
It arises from
- Lower one-third of the posterior side of the body of sternum.
- Posterior surface of the xiphoid process of the sternum.
- Posterior surface of the costal cartilages of lower three or four ribs.
The sternocostalis muscle is located behind the sternum at the inner aspect of front of the chest wall and with the exception of the first space, at costal cartilages within the anterior part of the upper intercostal spaces. In order to be inserted within the lower and inner surfaces of the costal cartilages of 2nd-6th ribs, the fibres separate as strips upwards and laterally. Sternocostalis is innervated by intercostal nerves. It helps in pulling down the costal cartilages.

 (53 votes, average: 4.57 out of 5)
(53 votes, average: 4.57 out of 5)