The trapezius is a flat regular triangular muscle on the back of the neck and the upper thorax.The muscles of two sides lie side by side in the midline and collectively create a diamond shape/ trapezoid shape, therefore the name trapezius.
Origin
- The point of inception is at a line that move throughout the medial third of the superior nuchal line at the base of the skull above to the external occipital protuberance
- It afterwards comes down around the posterior free edge of the nuchal ligament, the vertebral spinous processes to the twelfth thoracic vertebra, and the stepping in supraspinal ligaments.
- The line of origin is an upside-down
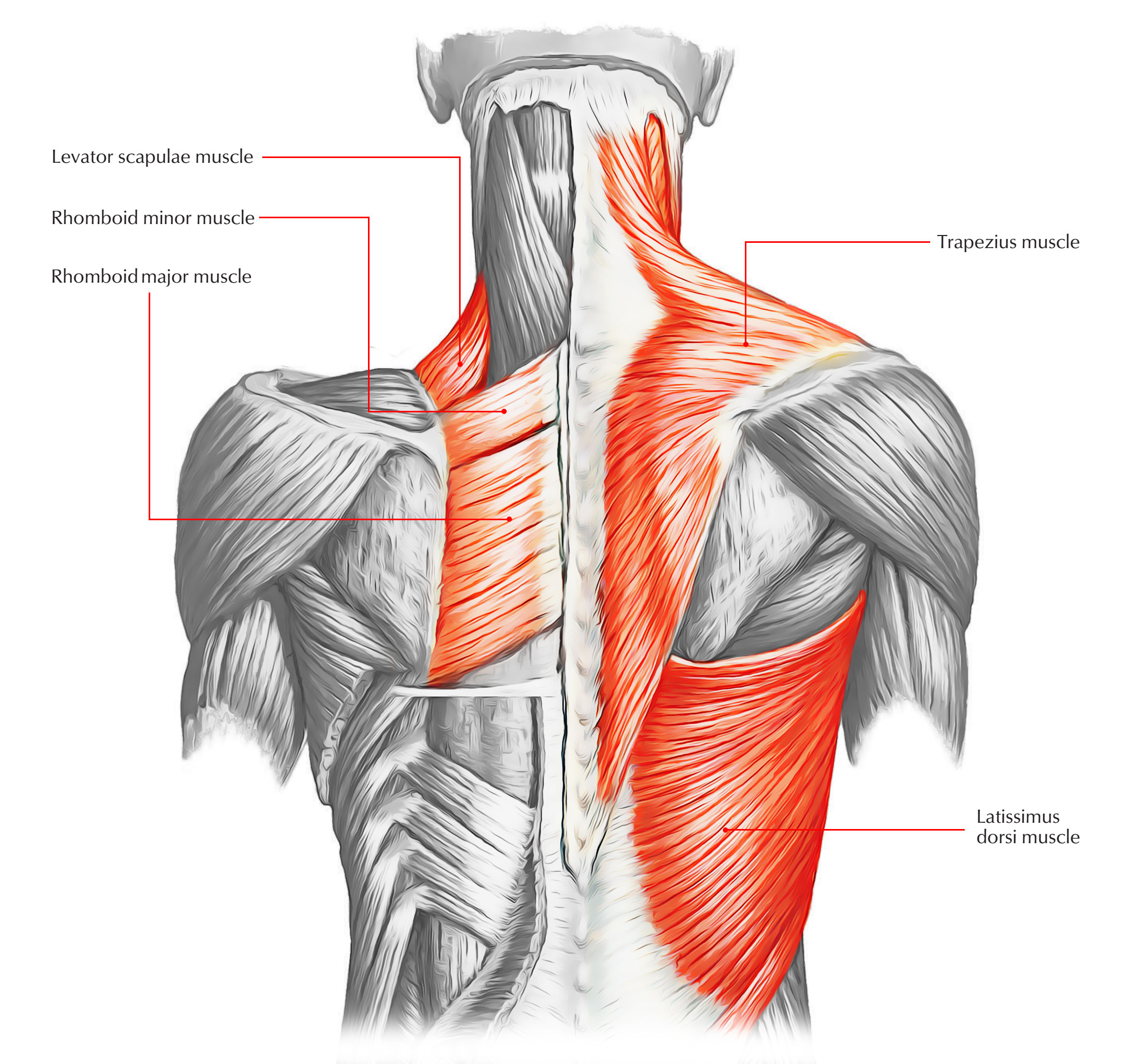
Trapezius Muscle
It emerges from:
- Medial third of the superior nuchal line,
- External occipital protuberance,
- ligamentum nuchae,
- Spine of 7th cervical vertebra, and
- Spines of all thoracic vertebrae
Insertion
As a constant line that
- Passes throughout the posterior border of the lateral third of the clavicle,
- Over the medial border of the acromion, and
- With the upper edge of the spine of the scapula (omitting the broadened triangular region at the spine’s medial end).
- With the lower edge of the spine of the scapula, ending at the tubercle of the spine, the line of attachment then doubles back over for a short length.
- Seen from above, the line of insertion is a V, directed laterally, on the top of the bony shoulder girdle.
The insertion takes place as follows:
- The superior fibers to be placed on to the posterior border of the lateral third of the clavicle, goes downwards and laterally.
- The middle fibers to be placed on to the medial margin of the acromion and upper lip of the crest of the spine of the scapula continue horizontally.
- The lower fibers to be placed on to the deltoid tubercle at the joint of medial and middle third of the spine of the scapula go on up and laterally.
Structure
- The trapezius is a substantial, broad, triangular muscle situated on the back of the chest, the top of the shoulder, and the hack of the neck.
- The upper fibers of the trapezius go on downward and outside The middle fibers pass horizontally outside; and the lower fibers pass up-ward and outside, heading towards the tubercle on the spine of the scapula through a small aponeurosis.
- The muscle differs in density in its different locations.
- The part on the back of the neck is quite thin
- It produces a muscular column on both side of the midline together with the deep semispinahs capitis muscle.
- In between these columns when the neck is upright, the nuchal ligament rests on the midline of the back of the neck, at the bottom of the vertical groove.
- In side view, the back analysis of the neck can be concave, directly, or convex. It ends up being a raised ridge when the head and neck are hexed forward.
NERVE SUPPLY
It is by:
- spinal part of the accessory nerve (gives motor supply),.
- Ventral rami of C3 and C4 (bring proprioceptive sensations).
Actions
- The upper fibers of trapezius elevate the scapula as in shrugging the shoulder together with levator scapulae.
- The middle fibers of trapezius withdraw the scapula as in bracing back the shoulder together with rhomboids.
- The lower fibers of trapezius depress the medial part of the spine of the scapula.
- Acting with serratus anterior, so that the arm can be abducted beyond 90 ° the trapezius turns the scapula forward.
Clinical screening
Palpate the trapezius while the shoulder is shrugged against the resistance. Failure to shrug (to increase) the shoulder is suggestive of muscle weak point.

 (61 votes, average: 4.89 out of 5)
(61 votes, average: 4.89 out of 5)