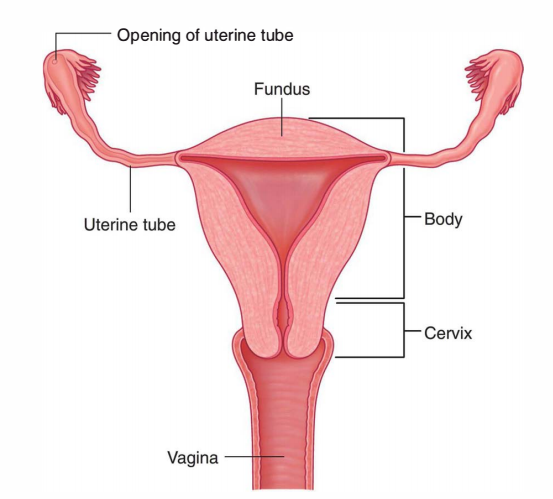
Uterine Tubes are the pair of ducts which carry ova from the ovaries to the uterine cavity. The uterine tubes are located in the upper free margin of the broad ligaments of the uterus and each uterine tube is about 10 cm long.
Uterine Tubes
External Features
Each of the two tubes has 2 endings and 4 parts.
Ends
Medial End
The uterine opening (ostium) is 1 millimeter in diameter and opens to the lateral angle of the uterine cavity.
Lateral (Fimbriated) End
It interacts with all the peritoneal cavity close to the ovary-by piercing the posterior layer of the broad ligament.
- It arches downward and inward partially to encircle the ovary.
- The abdominal ostium is 3 millimeters in diameter and its margin possesses atypical small fingerlike processes termed fimbriae. Thus it’s also referred to as fimbriated end.
Parts
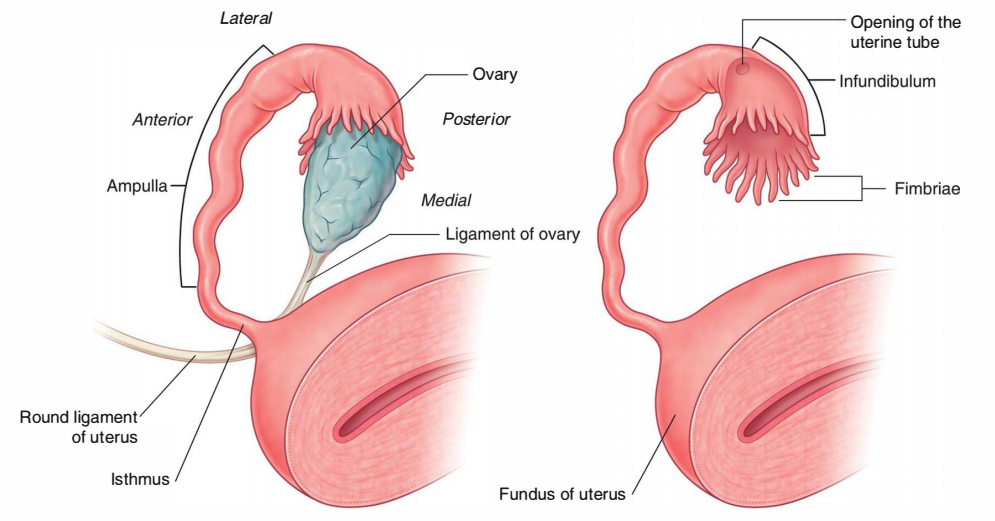
From lateral to medial end, the fallopian tube is split into four parts: infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus, and intramural.
Parts of the Uterine Tubes
Infundibulum (1 Cm Long)
- It’s the funnel-shaped lateral-most part which projects past the broad ligament of uterus.
- It overlies the ovary and presents an abdominal ostium.
- The circumference of the funnel is prolonged by changing some unusual processes termed fimbriae. One fimbria longer and more deeply grooved compared to the others is closely applied to the tubal extremity of the ovary and is referred to as an ovarian fimbria. The ovarian fimbria functions as a detector to time the release of the ovum. Just before the discharge of ovum fimbriae begin sweeping the surface of the ovary and ease the entry of ovum into the fallopian tube.
Ampulla (5 Cm Long)
- It’s the broadest and longest part of the pipe and creates quite more than one-half of the whole tube.
- It’s thin walled and tortuous.
- It’s the site of fertilization of the ovum.
Isthmus (2-3 Cm)
- It’s the narrowest part and is located just lateral to the uterus.
- It’s round and cord-like because of the thick muscular wall.
Intramural (Interstitial) Part (1 Cm Long)
It’s the section of uterine tube that traverses the uterine wall in the junction of fundus and body. It is located inside the wall of the uterus, thus the name intramural.
Structure of The Uterine Tube
From outside inward, the uterine tube contains 3 layers: serous, muscular, and mucous.
- The serous coating is originated from the peritoneum.
- The muscular layer is composed of smooth muscle that is ordered into inner circular and outer longitudinal layers.
- The mucous coating contains lining epithelium and underlying lamina propria.
The mucous membrane lining the tube presents about 6 primary longitudinal folds which in turn give rise to a number of secondary and tertiary folds. Consequently the lumen of the tube becomes highly atypical. This arrangement helps to supply nourishment to the zygote from all sides.
The lining epithelium is simple, ciliated columnar. It is composed of 2 types of cells: ciliated columnar cells and non-ciliated secretary cells. The secretion of secretary cells gives nutrients to the fertilized ovum. The cilia of ciliated cells beat toward the uterine cavity and assist in the transportation of the fertilized ovum.
Arterial Supply
Arterial Supply of the Fallopian tube
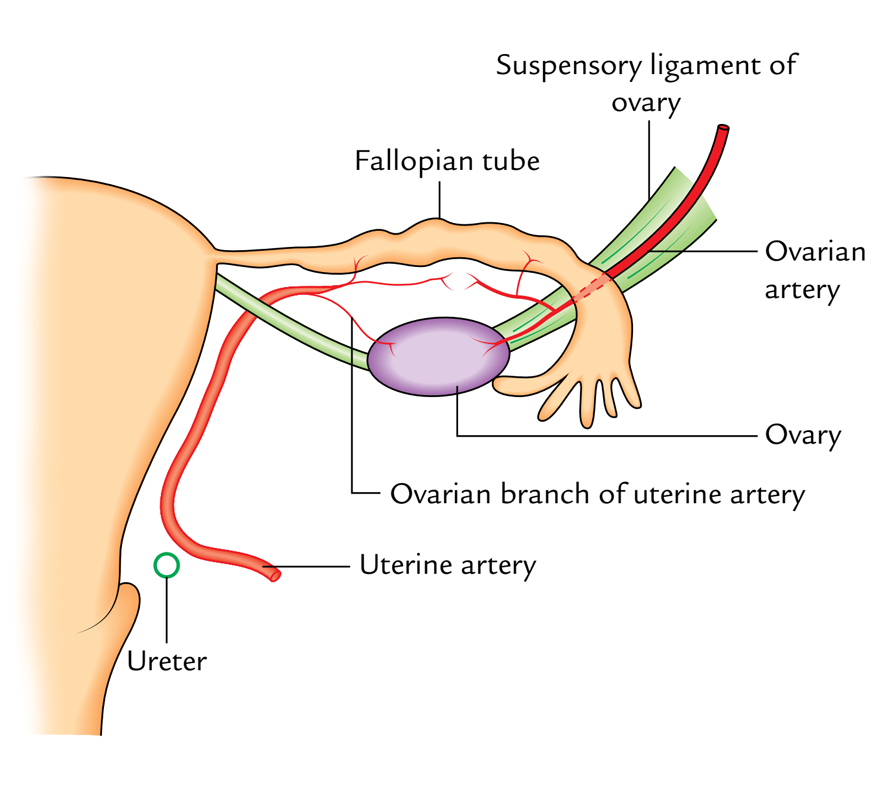
The fallopian tube is supplied by 2 arteries: ovarian and uterine arteries. Typically the medial two-third of the tube is supplied by the uterine artery and lateral one-third by the ovarian artery.
Venous Drainage
The veins correspond to arteries; thereby venous blood is drained by the ovarian and uterine veins.
Lymphatic Drainage
The lymph vessels follow the veins and drain into internal iliac lymph nodes, pre-aortic and para-aortic lymph nodes.
Nerve Supply
The tubes are supplied by both sympathetic and parasympathetic fibres. The sympathetic fibres are originated from ovarian and superior hypogastric plexuses. The preganglionic sympathetic fibres are originated from the T11 L2 spinal sections. The preganglionic parasympathetic fibres to the lateral part of the tube are originated from the vagus nerve and to the medial part from the pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2, S3, S4 spinal sections).
Clinical Significance
Salpingitis
The inflammation of the uterine tube (or salpinx) is referred to as salpingitis (salpinx: trumpet-like). It’s the commonest cause of tubal block resulting in secondary sterility in the female. Recently, the prevalence of tubal block has grown in modern females likely since they miss morning bath as a way to report on duty in time and waste time in makeup. Tubal infection typically happens because of upward spread of infection from vagina and uterus. The patency of tubal block is analyzed by these evaluations:
- Insufflation evaluation (or Rubin’s evaluation): Air is shoved into the uterus, and if the tube is obvious, the air leaks into the peritoneal cavity. The leakage of air creates hissing or bubbling sound which can be heard by a stethoscope over the iliac fossa.
- Hysterosalpingography: It’s a radiological technique where a radiopaque substance (example, Lipiodol) is injected into the uterus by a suitable canula. It summarizes the uterine cavity and uterine tubes, and if tubes are evident, the contrast medium spills into the peritoneal cavity.
Ectopic Pregnancy
It’s commonest in the uterine tube (tubal gestation) and is typically related to intraperitoneal hemorrhage, among the reasons for acute abdominal crisis in women of childbearing age. The hemorrhage happens because of rupture of the tube caused by enlarging conceptus.
Tubectomy
It’s a procedure for the female sterilization. In this process, every fallopian tube is ligated at 2 points and the section of tube between the ligatures is resected. This prevents the assembly of male and female gametes, thus no fertilization. This is the perfect approach to family planning in the female.

 (46 votes, average: 4.68 out of 5)
(46 votes, average: 4.68 out of 5)