Interrelated links of deep and superficial veins exist in the foot. The deep veins trail the arteries.
- Over the metatarsals, superficial veins channel into a dorsal venous arch on the dorsal surface of the foot.
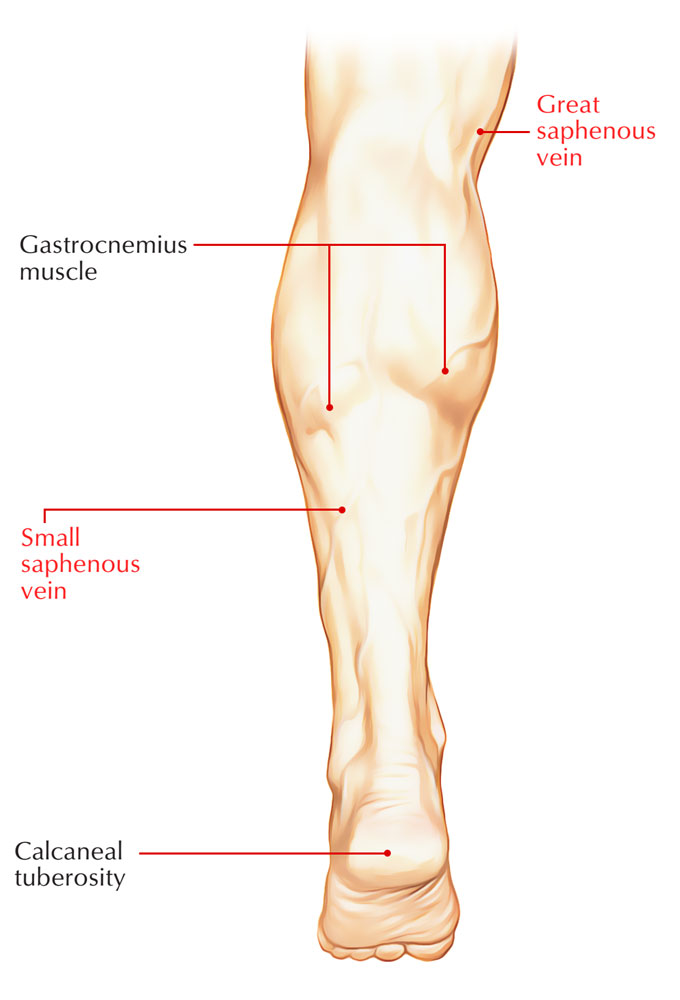
- The great saphenous vein emerges from the medial aspect of the arch and then travels anterior towards the medial malleolus and over the medial aspect of the leg.
- The small saphenous vein begins from the lateral part of the arch and then travels posterior towards the lateral malleolus and over the back of the leg.
Veins of foot
Great Saphenous Vein
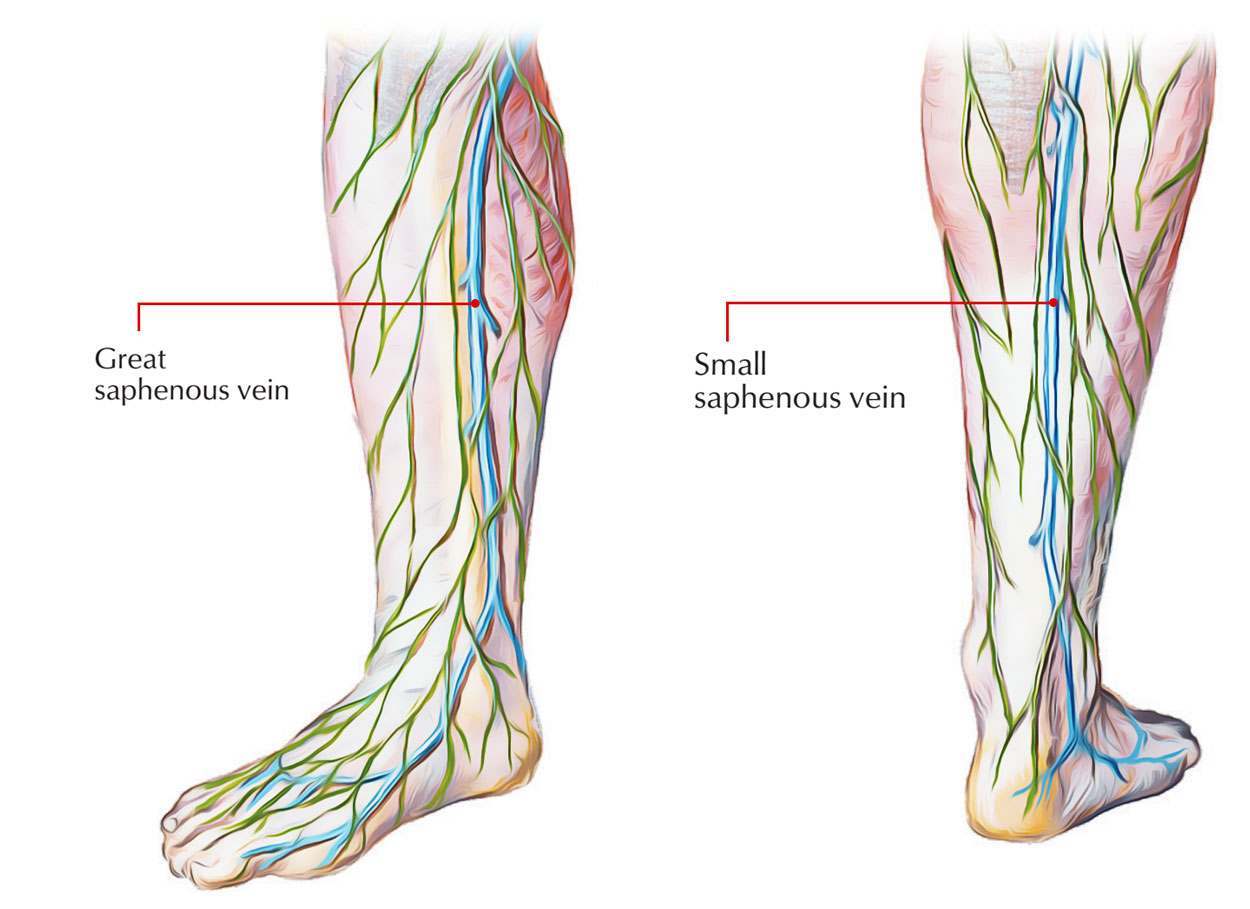
The great saphenous vein is found in the superficial fascia and is the longest vein of the body. It is also referred to as long saphenous vein.
Tributaries
- At the beginning: Medial marginal vein of the big toe.
- In the leg:
- Communicating veins among small saphenous and deep veins.
- Posterior arch vein – It collects the blood via the posteromedial part of the calf and also begins as a series of small venous arches linking the three medial ankle-perforating veins.
- Just below the knee:
- Anterior veins of the leg – They connect with the great saphenous vein and extend diagonally from the shin.
- From the calf, some veins connect with the small saphenous vein.
- In the thigh:
- Anterolateral vein – It starts in the lower part of the front of thigh, travels through the apex of femoral triangle, and afterwards in the upper part of the thigh, connects with the great saphenous vein.
- Posteromedial vein (accessory saphenous vein).
- Just before piercing the cribriform fascia:
- Superficial epigastric vein.
- Superficial circumflex iliac vein.
- Superficial external pudendal vein.
- These veins accompany the corresponding superficial branches of the femoral artery.
- Just before the termination in the femoral vein: the blood from the anterior part of the perineum is channed by the deep external pudendal vein.
Small (Short) Saphenous Vein
- Small (short) Saphenous Vein is formed by the combination of the lateral end of the dorsal venous arch, and the lateral dorsal digital vein of the little toe, inferiorly and posteriorly towards the lateral malleolus.
- On its lateral aspect, it goes along with the sural nerve, while it travels superiorly at the back of the lateral malleolus, alongside the lateral border of tendocalcaneus.
- Afterwards it pierces the deep fascia, travels in the middle of the back of the leg, and until it arrives at the middle of the popliteal fossa, it takes a subfascial path in the middle of the two heads of the gastrocnemius.
- Later it turns interiorly in order to terminate into the popliteal vein. While going deep to superficial, the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve goes along with the upper part of the vein. The small saphenous vein has 7-13 valves.
Veins of foot
Dorsal Venous Arch
The dorsal venous arch is located at the distal parts of the metatarsal bones. There are medial and lateral marginal veins, which drain both of the dorsal and plantar parts of the specific sides within the dorsal venous arch alongside the foot. It interacts along with proximally situated dorsal venous network and receives the dorsal digital as well as dorsal metatarsal veins.
This arch is drained as follows:
(i) Medial portion of dorsal venous arch receives dorsal digital vein via medial side of the great toe and is extended as medial marginal vein.
(ii) Lateral portion of dorsal venous arch gets dorsal digital vein through the lateral side of the little toe and is extended as lateral marginal vein.
Attachments
- Small saphenous vein: drains blood via the lateral dorsal venous arch along with posterior leg (calf) within the popliteal vein posterior towards the knee.
- Great saphenous vein: drains blood via the medial dorsal venous arch, leg, as well as thigh within the femoral vein just inferior towards the inguinal ligament.

 (49 votes, average: 4.88 out of 5)
(49 votes, average: 4.88 out of 5)