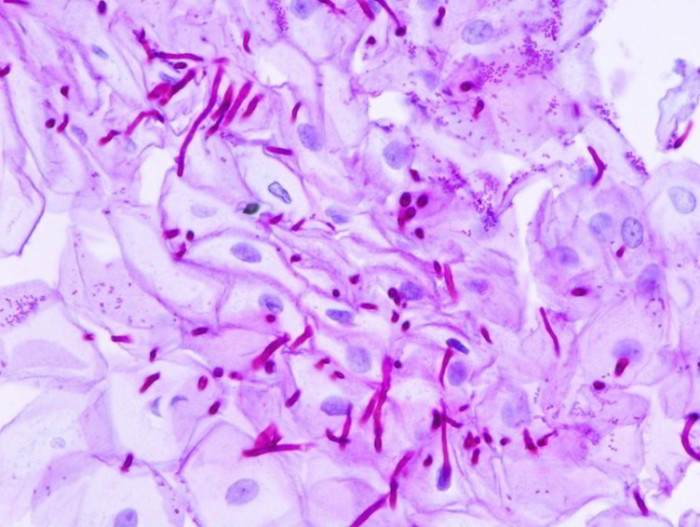
Candidiasis is a yeast infection that normally impacts just one part of the body but can be serious if it spreads around the body. In healthy individuals, the yeast Candida albicans usually exists on the surface of specific regions of the body, for example, mouth, throat and vagina. Occasionally, the yeast overgrows in localized regions, causing minor types of candidiasis for example oral thrush. In people who have decreased immunity, like those with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or diabetes mellitus, the yeast may disperse into the blood and other tissues. Disease that spreads through the entire body may also influence individuals
Who’ve long term urinary catheters or intravenous catheters, or those who have had prolonged courses of antibiotics or use intravenous drugs.
Extensive candidiasis may be diagnosed by culturing the yeast from a sample of blood or other body fluids or tissue samples. A chest X-ray might also be done to look for indications of disease in the lungs. Antifungal drugs may be given either orally or intravenously, determined by the severity of the disease.
Untreated, the disease can spread through the body and may eventually be deadly. The prognosis is dependent upon the extent of disease and on the man’s general well-being.

 (53 votes, average: 4.52 out of 5)
(53 votes, average: 4.52 out of 5)