Proteins play an important role in the body. Structural proteins make up substantial parts of all cells, and practical proteins, such as enzymes and hormones, straight manage cellular activities. Bear in mind that a protein is formed of a long chain of amino acids collaborated by peptide bonds. Protein synthesis includes positioning a particular amino acid in the proper position in the amino acid chain.
DNA and RNA are totally associated with the synthesis of proteins.
The Role of DNA
See the structure of DNA then continue. The 2 coiled hairs of nucleotides are signed up with by hydrogen bonds in between the nucleotide bases in each hair by complementary base pairing.Adenine (A) couple with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) couple with guanine (G).
The series of bases in a DNA molecule encodes details that identifies the series of amino acids in a protein More particularly, a series of 3 nucleotide bases (a triplet) in DNA encodes for a particular amino acid. For instance, a series of ACA encodes for the amino acid cysteine, while AGG encodes for serine. In this method, acquired details that identifies the structure of proteins is encoded in DNA.
The Role of RNA
In contrast to DNA, RNA includes a single hair of nucleotides. Each nucleotide includes among 4 nitrogenous bases: adenine, cytosine, guanine, or uracil(U). Keep in mind that uracil exists in RNA rather of thymine, which happens in DNA. RNA is synthesized in a cell’s nucleus by utilizing a strand of DNA as a template. Complementary pairing of RNA bases with DNA bases produces a hair of RNA nucleotides whose bases are complementary to those in the DNA molecule Uracil (U) in RNA couple with adenine (A) in DNA; adenine (A) in RNA couple with thymine (T) in DNA.
There are 3 types of RNA, and each plays an important role in protein synthesis.
Messenger RNA (mRNA) brings the genetic details from DNA into the cytoplasm to the ribosomes, the sites of protein synthesis. This details is brought by the series of bases in mRNA, which is complementary to the series of bases in the DNA design template.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and protein make up ribosomes, the sites of protein synthesis. Ribosomes consist of the enzymes needed for protein synthesis.
Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids to the ribosomes, where the amino acids are signed up with like a string of beads to form a protein There is a various tRNA for carrying each of the 20 type of amino acids utilized to construct proteins.
The characteristics of DNA and RNA
| DNA | R NA | |
| Strands | 2 strands signed up with by the complemen- | One |
| tary pairing of their nitrogenous bases | hair | |
| Sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Bases | Adenine | Adenine |
| Thymine | Uracil | |
| Cytosine | Cytosine | |
| Guanine | Guanine | |
| Shape | Helix | Straight |
Transcription and Translation
The process of protein synthesis includes 2 succeeding occasions: transcription, which happens in the nucleus, and translation, which takes place in the cytoplasm. In transcription, the series of bases in DNA identifies the series of bases in mRNA due to complementary base pairing. Therefore, transcription transfers the encoded details of DNA into the series of bases in mRNA. For instance, if a triplet of DNA bases is AGG, which encodes for the amino acid serine, the complementary paired triplet of bases in mRNA is UCC.
A triplet of bases in mRNA is referred to as a codon, and there is a codon for each of the 20 amino acids making up proteins Messenger RNA includes a chain of codons. Once it is synthesized, mRNA moves from the nucleus into the cytoplasm where it integrates with a ribosome, the site of protein synthesis. In translation, the encoded details in mRNA is utilized to produce a particular series of amino acids to form the protein As the ribosome moves along the mRNA hair, tRNA molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome and place them in the proper series in the forming polypeptide chain (protein) as defined by the mRNA codons.
Each tRNA molecule has a triplet of RNA bases called an anticodon at one end of the molecule Since there are 20 various type of amino acids making up proteins, there are at least 20 type of tRNA whose anticodons can bind with codons of mRNA. A tRNA molecule can just transport the particular amino acid that is encoded by the codon to which its anticodon can bond. For instance, a tRNA carrying the amino acid serine has the anticodon AGG that can bond with the mRNA codon UCC to place serine in the proper position in the forming amino acid chain. See figure 3.16 By transcription and translation, DNA identifies the structure of proteins, which, in turn, identifies the functions of proteins Transcription and translation might be summed up as follows:

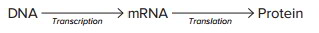

 (62 votes, average: 4.50 out of 5)
(62 votes, average: 4.50 out of 5)