The Vasa vasorum is found in large arteries as well as veins like the aorta along with its branches.
3-dimensional micro-computed tomography has shown that there are three different types of Vasa vasorum in human arteries via various vascular beds:
- Vasa vasorum internae emerge directly from the main lumen of the artery and then branch into the vessel wall.
- Vasa vasorum externae emerge from branches of the main artery and then dive back into the vessel wall of the main artery.
- Venous vasa vasorae emerge within the vessel wall of the artery but then drain into the main lumen or branches of concomitant vein.
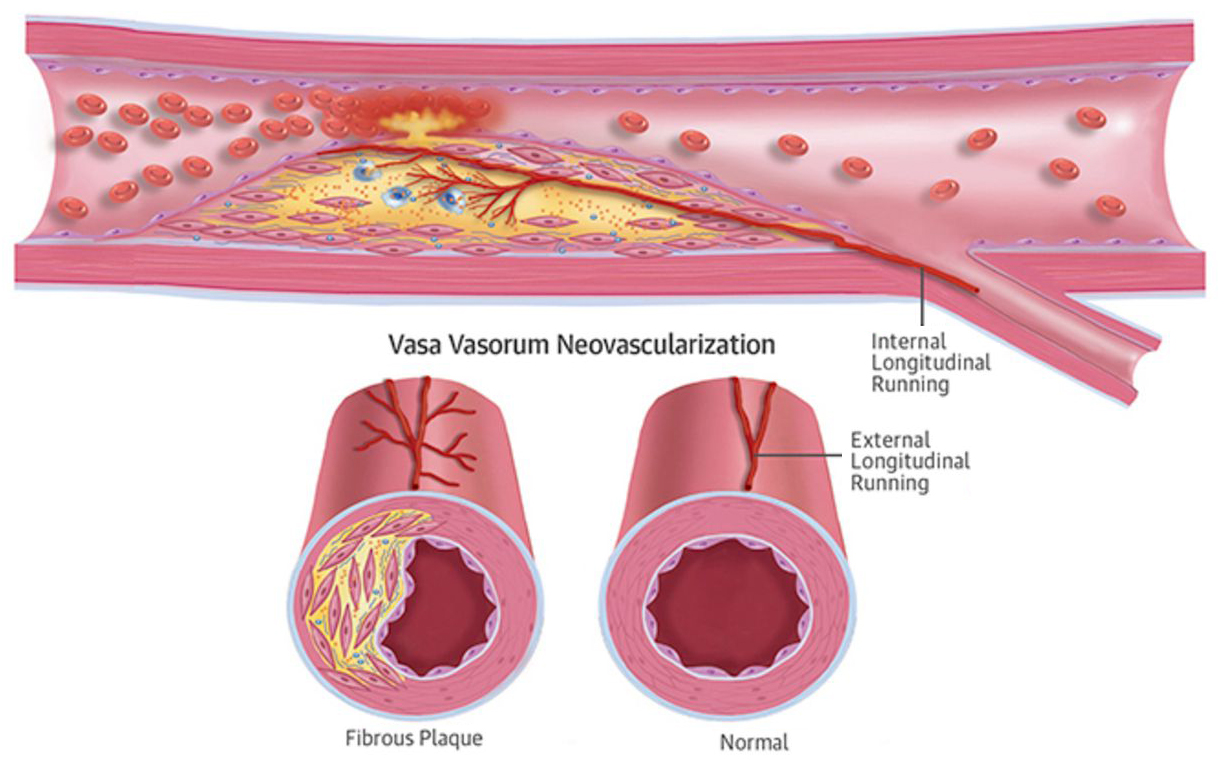
Vasa Vasorum
On the basis of the nature of Vasa vasorum, it pierces the vessel wall beginning at the Vasa vasorum interna or Vasa vasorum externa.
As a result of higher radial as well as circumferential pressures inside the vessel, wall layers nearby the main lumen of the artery, vasa vasorum externa cannot penetrate these sections of the vessel wall.
Clinical significance
Aortic Aneurysm
- In the human descending aorta, vasa vasorum terminates the supply of arterial walls at the level of the renal arteries with oxygenated blood.
- Therefore for its metabolic requirements, the aorta is dependent on diffusion underneath this location and is certainly distinctly slimmer.
- This increases the probability of aortic aneurysm at this location, specifically along with atherosclerotic plaques.
- Cerebral blood vessels are without vasa vasorum; on the other hand, these vessels possess rete vasorum, which have same utility as vasa vasorum.
Atheromatous Plaques
- There is a connection among changes in the vasa vasorum as well as the growth of atheromatous plaques.
- Damage by inflamed vasa vasorum cause necrosis inside the wall along with subsequent plaques development. Arteriosclerosis does not develop in arteries with thin walls that don’t have vasa vasorum.
Peripheral Nerve Diseases
For the most part, small vessels like vasa vasorum and vasa nervorum are vulnerable towards external mechanical compression. Therefore they are related to pathogenesis of peripheral vascular as well as nerve diseases.
Biological Indication
- In pathogenic process of giant cell arteritis, the T cells found near vasa vasorum are considered to be involved.
- In tertiary syphilis, Inflammation and succeeding destruction of the vasa vasorum causes syphilitic aortitis.
- Within vasa vasorum, existence of corkscrew collateral vessels is a symptom of Buerger’s disease as well as makes a distinction from Raynaud’s phenomenon.
- Obliterating endarteritis of the vasa vasorum causes aneurysm development in the thoracic aorta due to ischemia and fading of the aortic adventitia.

